Phytopharmacology in the Nanotech Era: Bridging Natural Compounds with Pharmaceutical Nanocarriers
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.64062/JPGMB.Vol2.Issue1.4Keywords:
Phytochemicals, Nanocarriers, Nanotechnology, Bioavailability, Targeted Delivery, Polymeric Nanoparticles, Lipid-Based Carriers, Natural Products, Phytopharmacology, Nanomedicine, Theranostics, Drug Delivery, Therapeutic Efficacy.Abstract
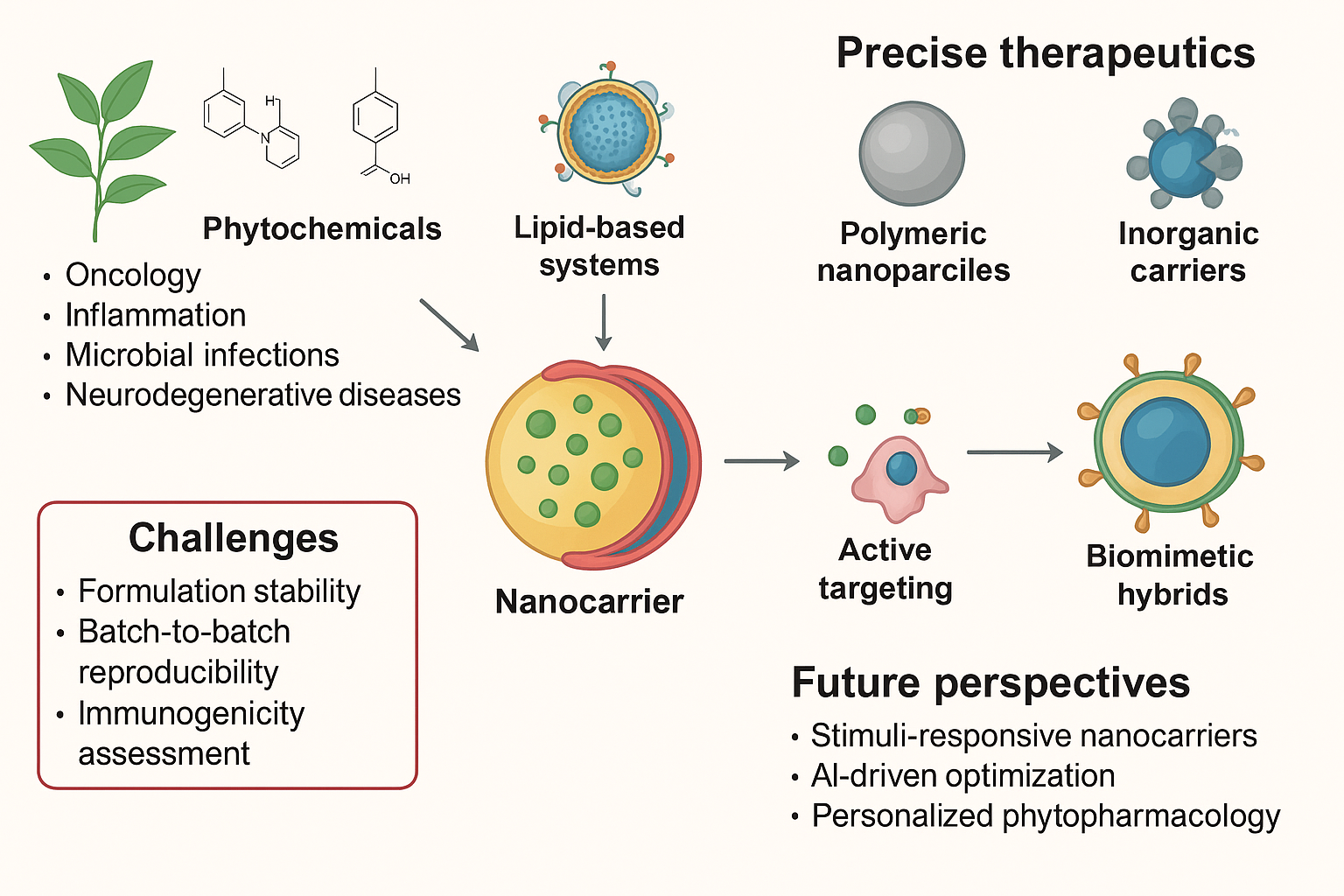
Phytochemicals derived from natural plant sources possess remarkable therapeutic potential across oncology, inflammation, microbial infections, and neurodegenerative diseases. However, their clinical translation has been severely limited by poor aqueous solubility, rapid hepatic metabolism, chemical instability, low bioavailability, and inadequate tissue targeting. The integration of nanotechnology with phytopharmacology represents a paradigm shift in natural product-based therapeutics, offering sophisticated nanocarrier platforms—including lipid-based systems, polymeric nanoparticles, inorganic carriers, and biomimetic hybrids—to overcome these inherent limitations. Nanocarriers enhance phytochemical solubility, provide controlled and sustained release kinetics, protect bioactive molecules from enzymatic degradation, and enable both passive and active targeting to disease sites. Advanced formulations such as curcumin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles, quercetin-functionalized lipid carriers, and pH-responsive delivery systems have demonstrated markedly improved pharmacokinetic profiles, tissue-specific accumulation, and therapeutic efficacy in preclinical and clinical studies. Furthermore, multifunctional nanoplatforms enable co-delivery of multiple phytochemicals and integration of diagnostic imaging agents for theranostic applications. Despite these advances, challenges including formulation stability, batch-to-batch reproducibility, immunogenicity assessment, regulatory standardization, and cost-effective scale-up require continued attention. Future perspectives emphasize smart, stimuli-responsive nanocarriers, artificial intelligence-driven optimization, personalized phytopharmacology, and environmentally sustainable synthesis methods. Collectively, phytochemical nanomedicines represent a transformative approach to unlocking the full therapeutic potential of plant-derived compounds, bridging traditional herbal medicine with modern precision therapeutics and enabling safer, more effective, patient-centric treatment modalities.