Plant-Derived Bioactive Compounds as Antidiabetic Agents: Therapeutic Mechanisms and Prospects
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.64062/JPGMB.Vol2.Issue1.3Keywords:
Herbal medicine, nanopharmacology, nanoparticles, targeted delivery, bioavailability, controlled release, phytotherapyAbstract
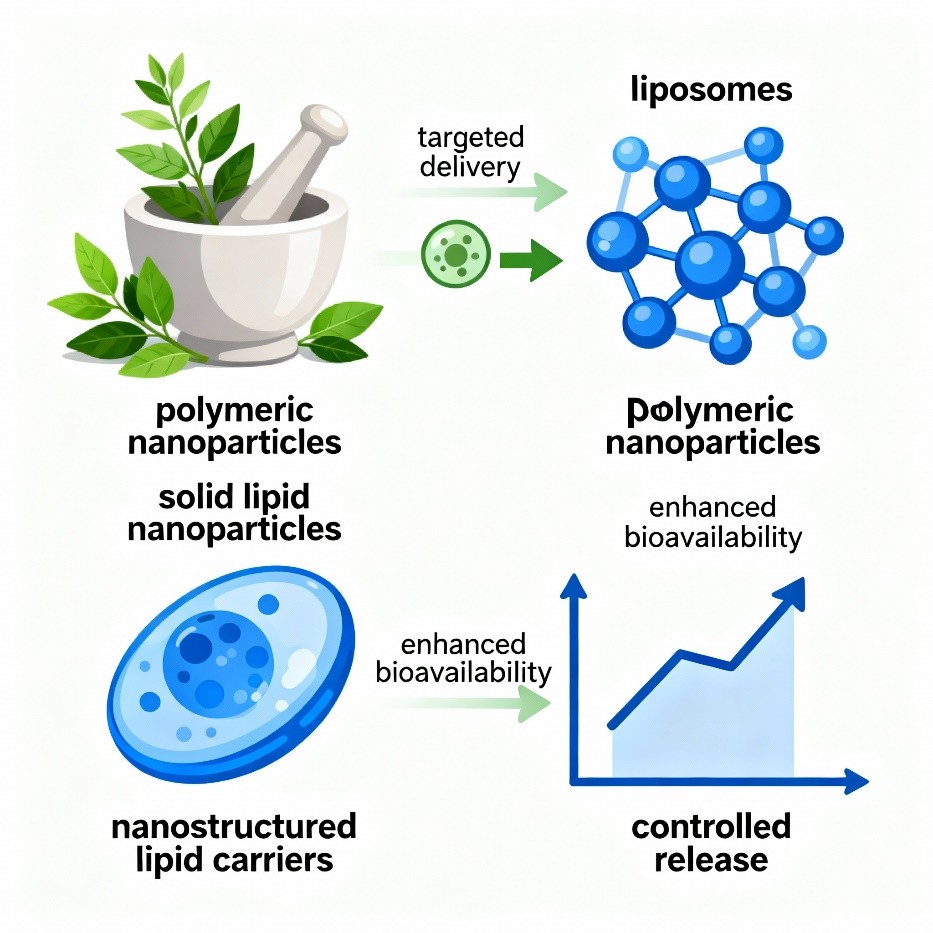
Herbal medicine has a long-standing history in the treatment of various ailments, but conventional formulations often suffer from poor solubility, low bioavailability, and variable pharmacokinetics. Integration of nanotechnology with herbal pharmacology—termed herbal nanopharmacology—offers solutions to these limitations, enabling targeted delivery, controlled release, and enhanced therapeutic efficacy. This review explores recent advances in herbal nanocarriers, including liposomes, polymeric nanoparticles, solid lipid nanoparticles, and nanostructured lipid carriers, focusing on formulation strategies, characterization techniques, pharmacological applications, and clinical translation challenges. Future perspectives emphasize precision herbal therapy, synergistic formulations, and regulatory considerations.