Novel Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.64062/JPGMB.Vol1.Issue6.4Keywords:
Alzheimer’s disease, early diagnosis, biomarkers, cerebrospinal fluid, blood-based biomarkers, mild cognitive impairment, amyloid-beta, tau, miRNA.Abstract
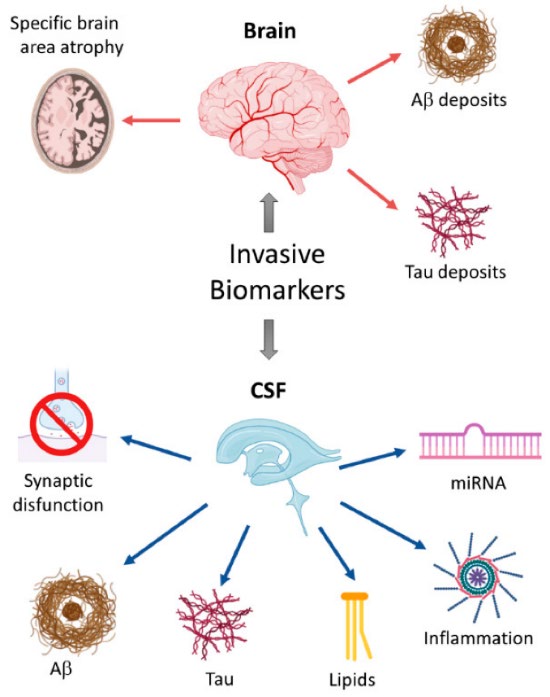
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease for which early detection is essential but frequently difficult because of intrusive and expensive diagnostic techniques. The purpose of this study was to assess new biomarkers for AD early detection in blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). 120 participants, ages 55 to 80, participated in a cross-sectional observational study that included patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI), early-stage AD, and cognitively normal controls. Biomarker analyses, such as amyloid-beta (Aβ42), total tau, phosphorylated tau, neurofilament light chain (NfL), and miRNA panels, were conducted in addition to cognitive tests (MMSE and MoCA). The findings revealed a progressive decline in cognitive function and notable changes in biomarker levels among groups, with tau, phosphorylated tau, NfL, and miRNA levels rising with the severity of the disease and Aβ42 falling. Strong correlations between biomarkers and cognitive scores as well as statistically significant group differences were validated by one-way ANOVA and Pearson correlation analyses. These results support the use of blood and CSF biomarkers in clinical screening and intervention strategies by highlighting their potential as sensitive, minimally invasive tools for early AD diagnosis.