Targeting Inflammatory Pathways in Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.64062/JPGMB.Vol1.Issue6.2Keywords:
Rheumatoid Arthritis, Inflammatory Pathways, Cytokine Inhibition, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1, JAK-STAT Signaling, NF-Κb, MAPK, PI3K/Akt, Animal Models.Abstract
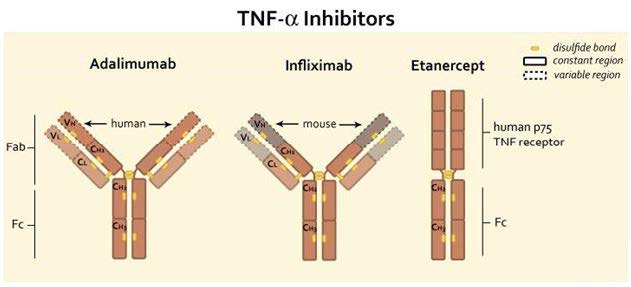
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by chronic inflammation of the synovium, cartilage and bone erosion and is mediated in large part by maladaptive inflammatory mechanisms. The preclinical analyses on animal models such as collagen induced arthritis (CIA), adjuvant induced arthritis (AIA) and transgenic mice on TNF have given necessary knowledge on the molecular basis of RA pathogenesis and treatment protocols. This review is a synthesis of the existing evidence on the use of these models in order to target key pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF- α, IL- 6, IL- 1) and intracellular signaling cascades (JAK -STAT, NF- - 00, MAPK, PI3K/Akt) to reduce joint inflammation, osteoclast activity, and tissue damage. Also, the use of emerging strategies like nanoparticle-based drug delivery delivers a tissue specific target, drug stability and less systemic toxicity. These preclinical studies are critically examined in terms of strengths, limitations and translational potential, combination and multi-target studies are proposed to counter-act redundancy in pathways, and gaps in future studies are highlighted. At last, these results indicate the critical role of animal models in informing the design of new therapeutic interventions that are more effective and safer to use in the treatment of RA.