Current Challenges in The Treatment of Autoimmune Disorders
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.64062/JPGMB.Vol1.Issue5.7Keywords:
Autoimmune Disorders, Animal Models, Immunotherapy, Disease Pathophysiology, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Type 1 Diabetes, Therapeutic Challenges, Immunomodulation.Abstract
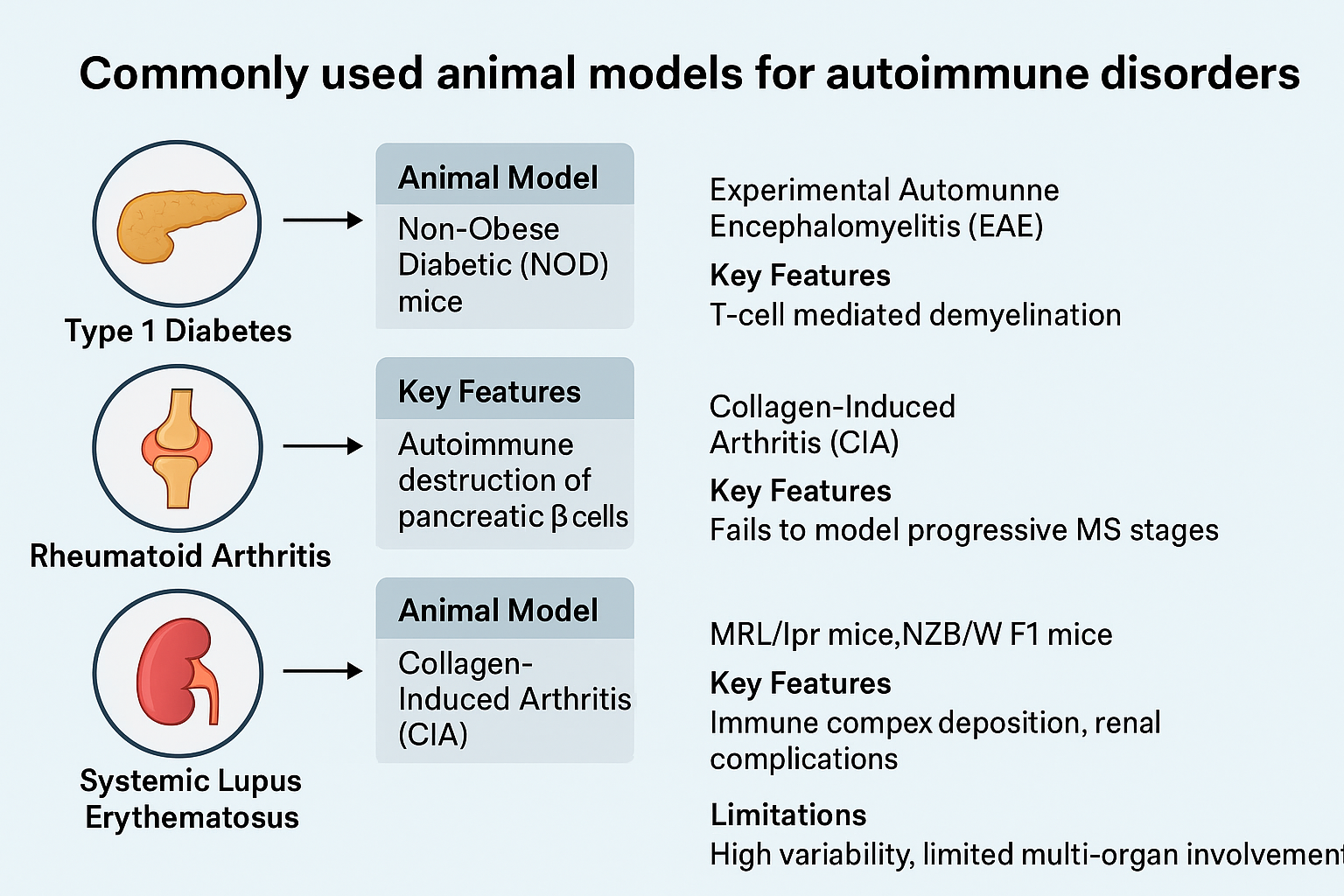
The broad and diverse category of chronic diseases known as autoimmune disorders is caused by the body's immune system mistakenly attacking its own cells and tissues, which leads to tissue damage, organ failure, and persistent inflammation. Because of their complex etiology, which includes genetic, environmental, and immunological variables, these disorders—which include multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and type 1 diabetes—present serious therapeutic issues. There has been little progress in creating long-lasting and efficient medicines, even with significant advances in immunology and therapeutic approaches. Understanding the pathophysiology of diseases, assessing immunomodulatory tactics, and forecasting the possible effectiveness of new treatments have all benefited greatly from the use of animal models. This review focuses on the current difficulties in treating autoimmune disorders as they have been identified by animal-based research. These difficulties include species-specific immune responses, translational gaps between preclinical and clinical outcomes, variability in disease manifestation, and limitations of current preclinical models. Additionally, it talks about methodological strategies, the advantages and disadvantages of various animal models, and new discoveries in treatments meant to alter immune responses.