Advances In Stem Cell Therapy for Cardiovascular Diseases
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.64062/JPGMB.Vol1.Issue5.4Keywords:
Cardiovascular Diseases, Stem Cell Therapy, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Cardiac Stem Cells, Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells, Cardiac Regeneration, Paracrine Signaling, Biomaterial ScaffoldsAbstract
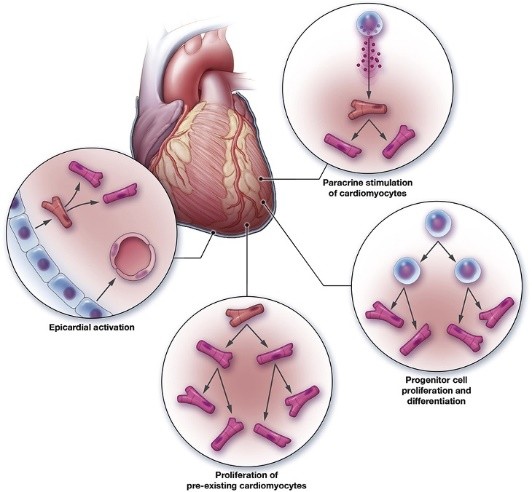
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are a major global health concern, but current treatment methods mostly aim at alleviating symptoms rather than repairing damaged heart tissue. It has been suggested that stem cell therapy might be a viable regenerative option for restoring cardiac function by direct differentiation, paracrine signaling, immunomodulation, and angiogenesis. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), cardiac stem cells (CSCs), and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have therapeutic potential, according to preclinical study. Biomaterial scaffolding and improved delivery methods also lead to improved cell survival, retention, and integration. Although the outcomes are encouraging, shortcomings associated with this approach include low long-term engraftment, immune rejection, tumorigenicity, and inconsistency in outcomes, which discourage clinical translation. Current studies that have aimed to address these limitations through improved cell selection, combination therapy, biomaterials engineering, and personalized therapies, promise to overcome these obstacles and provide the community with the possibility to transform cardiovascular care beyond palliative care to actual myocardial regeneration.