Influence of HLA Alleles in Adverse Drug Reactions: A Pharmacogenetic Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.64062/JPGMB.Vol1.Issue4.11Keywords:
Adverse Drug Reactions (Adrs), Hla Alleles, Hypersensitivity, Transgenic Mouse Model, Carbamazepine, Abacavir, AllopurinolAbstract
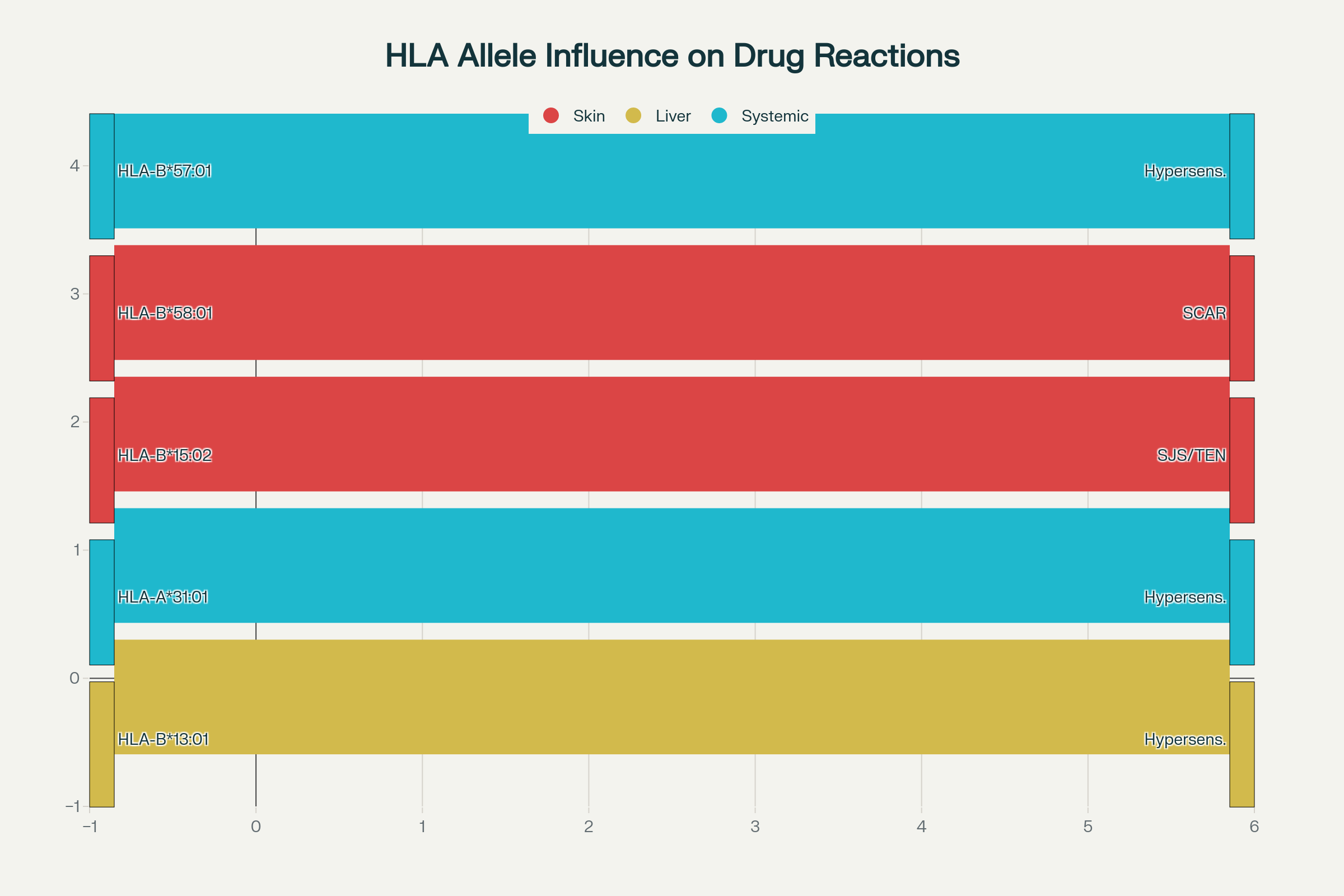
Adverse drug reactions (ADRs) especially immune mediated ADRs are a major challenge to clinical pharmacology and drug development. There is a mounting evidence that certain alleles of the Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) such as HLA-B15:02, HLA-B57:01 and HLA-A*31:01 predispose individuals to severe hypersensitivity reactions when exposed to carbamazepine, abacavir, and allopurinol, respectively. The use of transgenic mouse models that express these HLA alleles in this pharmacogenetic study was utilized to understand their contribution in the pathogenesis of immune-based ADRs. In transgenic mice, the rate of hypersensitivity symptoms was significantly higher after drug administration, and the concentration of cytokines (especially TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma) in the serum was higher, as well as T-cell activation (CD69+, CD25+) compared to the control mice. Immune-mediated tissue inflammation in HLA-expressing groups was further confirmed using histopathological evaluations. The results they report are highly representative of known clinical trends in humans and give direct in vivo support to the relationship between HLA polymorphisms and drug-induced immunotoxicity. The analysis shows the usefulness of HLA-transgenic mouse as predictive model of preclinical immunogenicity profiling that can be incorporated into the early stage drug safety testing and development of personalized medicine.